Home > Education > Contaminants & Risks > Drinking Water Contaminants > Emerging Chemical Contaminants
|
What are Emerging Chemical Contaminants?
Emerging contaminants are chemicals that are new or have increased in the last 20 years. These materials may also be called Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs), because members of the research community believe they are potentially hazardous. CECs are typically unregulated (or lack sufficient management) and require more research to better understand the human and ecological risks. Continue reading to learn about some of the better-known emerging contaminants, including: Chromium-6, which gained attention following the 2000 film, Erin Brokovich; PFAS, also known as the forever chemicals; and endocrine-disrupting compounds. |
Image Credit: NGI
|
WQRF Research
The WQRF study, Emerging Contaminant Removal and Microbial Growth, investigated removal efficiencies for 3 PFAS chemicals (PFOS, PFBS, PFHxS). Reverse Osmosis membranes removed 97.8%-99.9% of all PFAS tested, while Activated Carbon filters removed 98.1%-99.9% of the PFAS chemicals.
The WQRF study, Emerging Contaminant Removal and Microbial Growth, investigated removal efficiencies for 3 PFAS chemicals (PFOS, PFBS, PFHxS). Reverse Osmosis membranes removed 97.8%-99.9% of all PFAS tested, while Activated Carbon filters removed 98.1%-99.9% of the PFAS chemicals.
|
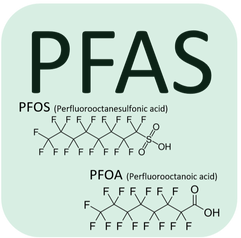
PFAS
PFAS (Perfluoroalkyl substances): a group of chemicals, including PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) & PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) Health Effects
Unclear, early research suggests a small increase in risk of testicular, kidney, and thyroid cancers |
Overview
PFAS are a group of chemicals used broadly in manufacturing and consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, water- and stain-repellent clothing, food packaging, and more. They are known as the "forever chemicals" due to the fact that they break down slowly over time. Blood tests show that Americans have been universally exposed. There are thousands of PFAS chemicals, however, concentrations have been decreasing as many major manufacturers voluntarily phased these chemicals out of production. On April 10, 2024, the EPA implemented new national primary drinking water standards aimed at protecting people from environmental PFAS exposures. |
|
Chromium-6
Also referred to as Chromium VI, Hexavalent Chromium, CR(VI) Health Effects
High levels - skin ulcers, kidney and liver failure Low-level & chronic exposure - potentially increases risk of cancer |
Overview
Chromium-6 is used in manufacturing for steel processing and as an anticorrosive agent. Total chromium levels are regulated by the USEPA under the Primary Drinking Water Standards. While a lower limit may be needed, this goal may be beyond the capacity of municipal water treatment facilities and progress towards control of CR(VI) has been slow. |
|
Endocrine Disrupting Compounds (EDCs)
Health Effects
Lower sperm counts, undescended testicles, early puberty, thyroid dysfunction, potential effects on offspring. |
Overview
EDCs can mimic natural hormones and block cell receptor sites or trigger actions, altering the body’s natural growth and development. |
Agents known to have endocrine-disrupting capabilities.
|
Endocrine Disruptor - Designated Use
|
Endocrine Disruptor - Designated Use
|
|
Overview of Regulated & Emerging Chemical Contaminants in the U.S.
With Kelly Reynolds, PhD |
Emerging Contaminants &
Mixed Exposures Marc Verhougstraete, PhD Interview |
A Water Quality Expert Weighs in on Emerging Contaminants
Joan Rose, PhD Interview |