What is Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Why is it Important?
|
About Reverse Osmosis
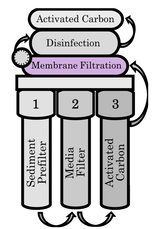
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a process where water and contaminants are separated by passage through a thin semipermeable membrane. The membrane creates a barrier between water molecules and chemical or microbial contaminants as high-pressure forces water through the membrane, leaving contaminants behind. RO systems can remove most organics, metals and nitrate but are often used in succession with activated carbon and UV light for increased efficiency and for removal of inorganic compounds. This multibarrier approach eliminates a wide variety of contaminants that no single system can fully address. Proper Use of Pre-Filters The use of carbon pre-filters before RO systems is standard in home treatment units to extend the life of the RO membrane and reduce membrane fouling. Proper maintenance of an RO system and the pre-filters are essential for reliable treatment, as treatment efficiency is known to decrease over time. The integrity of the RO membrane is typically monitored by measuring conductivity, since it is directly proportional to the dissolved solid content in water. A properly maintained residential RO system should remove more than 90% of dissolved solids. |
Certified Treatment Devices Click here to search for water treatment devices that have been certified to NSF/ANSI standards. Certification ensures that the device is made from safe materials and the contaminant reduction claims listed on the packaging are verified by independent lab testing. Example of a multi-barrier system with RO membrane filtration
Example of a reverse osmosis system
|
|
Benefits
|
Limitations
|